Lipid Disorders
Understanding Lipid Disorders:
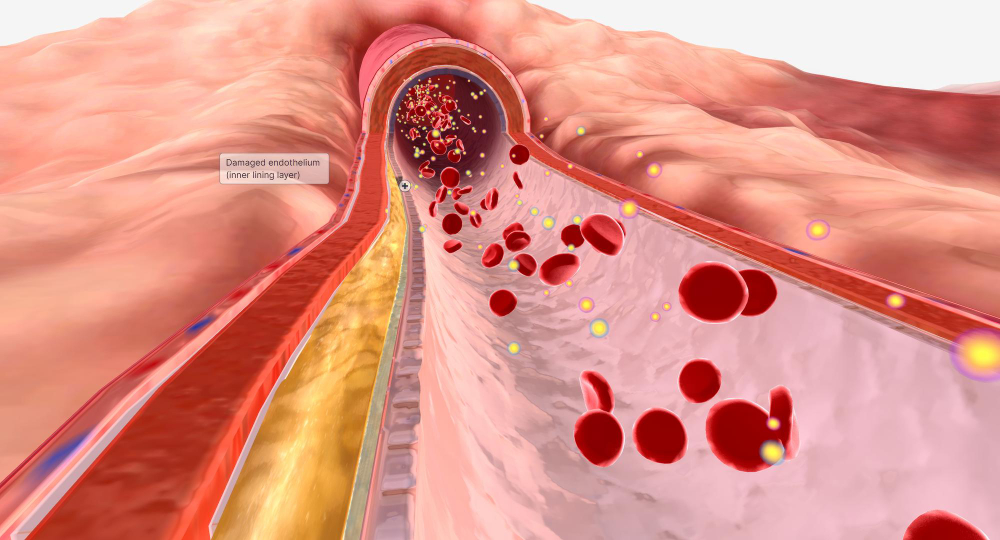
Lipid disorders, specifically hyperlipidemia, are conditions characterized by abnormal levels of lipids (fats) in the bloodstream. These lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides, which are essential for various bodily functions but can pose health risks when present in excessive amounts. Hyperlipidemia is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, coronary artery disease, heart attack, and stroke.
Diagnosis: Diagnosing lipid disorders involves measuring lipid levels in the blood through a simple blood test called a lipid panel or lipid profile. This test typically assesses levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and triglycerides. Based on these measurements and established guidelines, healthcare providers can determine whether an individual has hyperlipidemia and assess their risk of cardiovascular disease.
Management Strategies: Managing lipid disorders focuses on reducing lipid levels to optimal ranges and minimizing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Here are key components of lipid disorder management:
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Heart-Healthy Diet: Adopting a diet low in saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity such as aerobic exercise, strength training, or cardiovascular workouts to improve lipid levels and overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight through calorie control, portion control, and regular exercise can help improve lipid profiles.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking is essential for individuals with lipid disorders, as smoking can worsen lipid levels and increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Limiting Alcohol Intake: Moderating alcohol consumption, as excessive alcohol intake can raise triglyceride levels and contribute to lipid disorders.
Medication Management:
- In addition to lifestyle modifications, medications may be prescribed to lower lipid levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events. Common classes of lipid-lowering medications include statins, ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors, fibrates, and niacin. The choice of medication depends on factors such as lipid levels, cardiovascular risk, and individual patient characteristics.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up:
- Regular monitoring of lipid levels through follow-up lipid panels and clinic visits is essential to track progress, adjust treatment as needed, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.
