What is Cardiomyopathy?
Cardiomyopathy is a heart condition where the heart muscle doesn't work right. It might get too thick, too big, or too stiff, which makes it tough for the heart to pump blood the way it should.
This can cause different health issues and may even lead to heart failure. Some people might need medication or even a heart transplant to manage this condition.
Types of Cardiomyopathy
- Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: This type happens when parts of the heart muscle thicken more than they should. This thickening can block the lower chambers of your heart, making it hard for your heart to pump blood effectively.
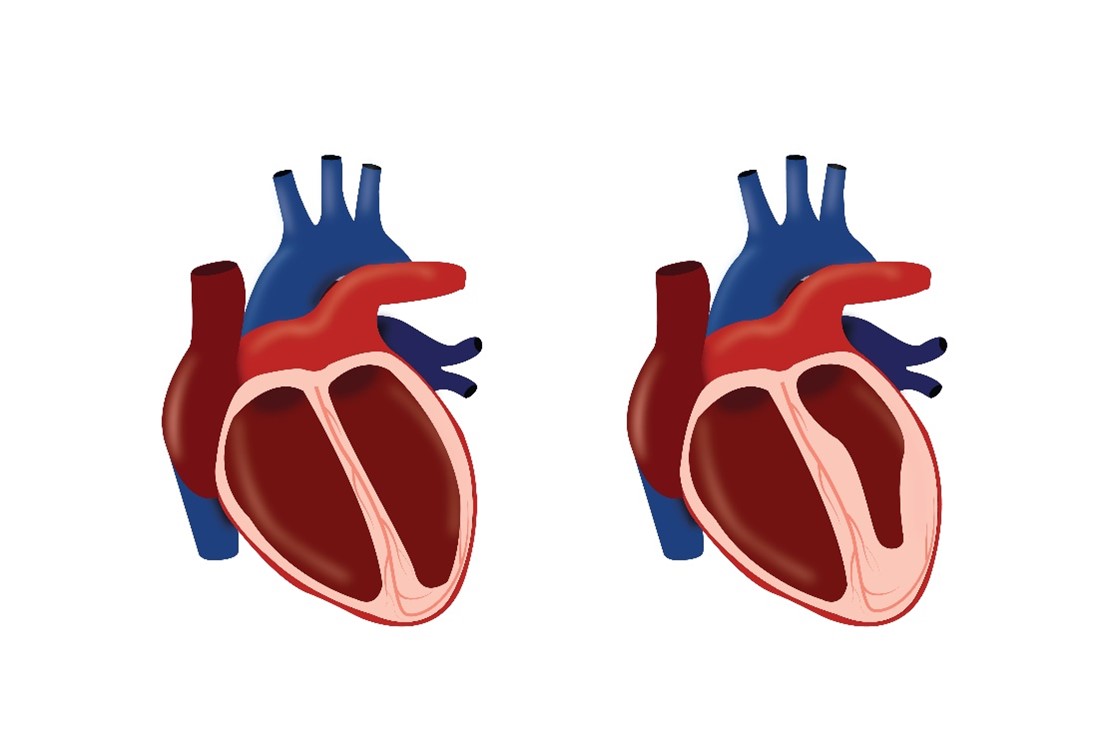
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy: This common form of cardiomyopathy occurs when the lower chambers of the heart become weak and enlarged.
- Peripartum Cardiomyopathy: This rare but serious condition can develop during the late stages of pregnancy or shortly after giving birth.
- Restrictive Cardiomyopathy: This type makes the heart's lower chambers stiffen without thickening, which means they can't relax and fill with enough blood.
- Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy (Broken Heart Syndrome): Often triggered by severe stress, this condition mostly affects women post-menopause.
Each type of cardiomyopathy has unique effects on the heart and needs specific attention from doctors.
Cardiomyopathy symptoms can include:
- Chest pain that occurs after physical exertion or eating large meals
- Heartbeats that may feel fast, strong, or irregular
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, feet, abdomen, and the veins in the neck
- Abdominal bloating caused by fluid accumulation
- Coughing when lying down
- Difficulty sleeping flat due to discomfort
- Episodes of fainting
Symptoms generally worsen if not managed. The progression of the condition can vary greatly from person to person; for some, it may deteriorate quickly, while for others, it may remain stable for a long time.
How is Cardiomyopathy Diagnosed?
If your doctor thinks you might have cardiomyopathy, they will check your health history and give you a physical exam. You might also be sent to a heart specialist called a cardiologist. The cardiologist will do more tests, like heart scans and blood tests, to see how your heart is functioning.
How is Cardiomyopathy Treated?
While there's no cure for cardiomyopathy, there are treatments that can help control its symptoms and slow down the disease. Treatment options may include making some lifestyle changes, like adjusting your diet and getting more exercise, taking medications to help your heart function better, and possibly getting a device implanted to help regulate your heartbeat.
"Feeling out of breath or unusually tired? Don’t wait talk to your doctor about heart health and cardiomyopathy screening today."